
International Journal of Scientific Research and Management (IJSRM)
||Volume||5||Issue||07||Pages||6014-6018||2017||
Website: www.ijsrm.in ISSN (e): 2321-3418
Index Copernicus value (2015): 57.47 DOI: 10.18535/ijsrm/v5i7.26
Dr.G.Sasikumar, IJSRM Volume 5 Issue 07 July 2017 [www.ijsrm.in] Page
6014
Mobile Banking and Security Challenges
Dr.G.Sasikumar
Asst.Professor,
PG Department of Economics and Management Studies,
Maruthupandiar College of Arts & Science,
Vallam, Thanjavur, Tamilnadu,
Abstract: Banking services have expanded from cash in the bank to internet banking and now mobile banking which attained broad
recognition internationally. With help of mobile banking facilitates the customers access their accounts and entire information about
bank products and services anywhere anytime through Internet and World Wide Web. The mobile banking is trustworthy, secured and cost
effective, nevertheless complex and vulnerable to network problem. Security issues are significant since intruders makes others life as
unsafe and miserable. One could be sufferer of a cyber crime in several ways. In this paper an effort is made to study the various security
issue, challenges and solutions related to mobile banking services.
Keywords: Mobile phones, Mobile banking, Cyber crime, Internet, Security.
1. Introduction
Banking services have been a division of society for long a
period. The conventional banking services need physical
interactions between customers and banks. Though, mobile
technology has brought banking services to next level. In
recent years, more number of people using banking services
and also modern mobile banking services. Mobile banking is
one of the gifts to human beings by Information and
Communication Technology. The term mobile banking refers
to the use of mobile device to access bank account and
perform online banking tasks such as checking balances,
transferring funds, bill payments etc [11]. Mobile usage has
observed an explosive growth in most of the Asian Economies
like India, China and Korea. In fact Korea possesses about a
70% mobile penetration rate and with its technical study
population has seen one of the most aggressive rollouts of
mobile banking services. Still, the main reason that mobile
banking scores over internet banking is that it enables
access computer
terminal to access their banks, they can now do so on the go
when they are waiting for their bus to work, when they are
travelling or when they are waiting for their orders to come
through in a restaurant. Globally, banks offer a variety of
mobile banking services; and those banks that do not currently
provide m-banking services claim they plan to do so in the
near future to remain relevant, according to a recent survey
conducted by the Aite Group. According to a study from the
University of Hamburg, Germany, m-banking mobile applica-
tions are growing exponentially; roughly 69% of banks already
offer such services.
A major challenge for the adoption of mobile banking
technology and services is the perception of insecurity. In the
survey conducted by the Federal Reserve, 48% of respondents
study, respondents were asked to rate the security of mobile
banking for protecting their personal information and 32%
rated it as somewhat unsafe and very unsafe, while 34% were
not sure of the security. These statistics represent a significant
barrier to the use of mobile banking products and services.
In this paper mobile banking services, challenges in mobile
banking, cyber crime and solutions are analyzed. The rest of
this paper is organized as follows. Section 2 offers literature
review of mobile banking, section 3 explains about the role of
mobile phones in daily routine life and mobile banking
services, section 4 presents the cyber crime problems with
mobile banking. The importance of mobile banking security
and preventive measures for mobile banking are illustrated in
section 5 and section 6 concludes this paper.
2. Literature Review
The Internet is one of the biggest blessings to manhuman
society by technology. One just cannot imagine the life
without the internet. Everyone wants to stay connected with
the Internet all the time through the mobile phones easily. The
mobile phones let users enjoy the social media on the go. A
major part of modern world is addicted to social networking
sites. The growth of every economy depends on various
sectors like agriculture, manufacturing, education, technology,
finance etc. Emerging and fast growing innovations in
information technology and globalization have changed the
whole process of service providing organizations. Innovative
information technology is the backbone of economic
development of any country. Globalization, competitive
pressure, and technology advancement change the whole
process of banking industry.
Now a days, the information and communications technology
have undergone through rapid development. In addition to that
the revolution of wireless technology and the intensive
penetration of mobile phones have encouraged banking
industries around the world and to invest considerably large
budget on building mobile banking systems, through the
adaption of different kinds of strategies with the aim of
attracting customer intention to use this new technology [19],
[21]. Consequently, the most popular banking systems that can
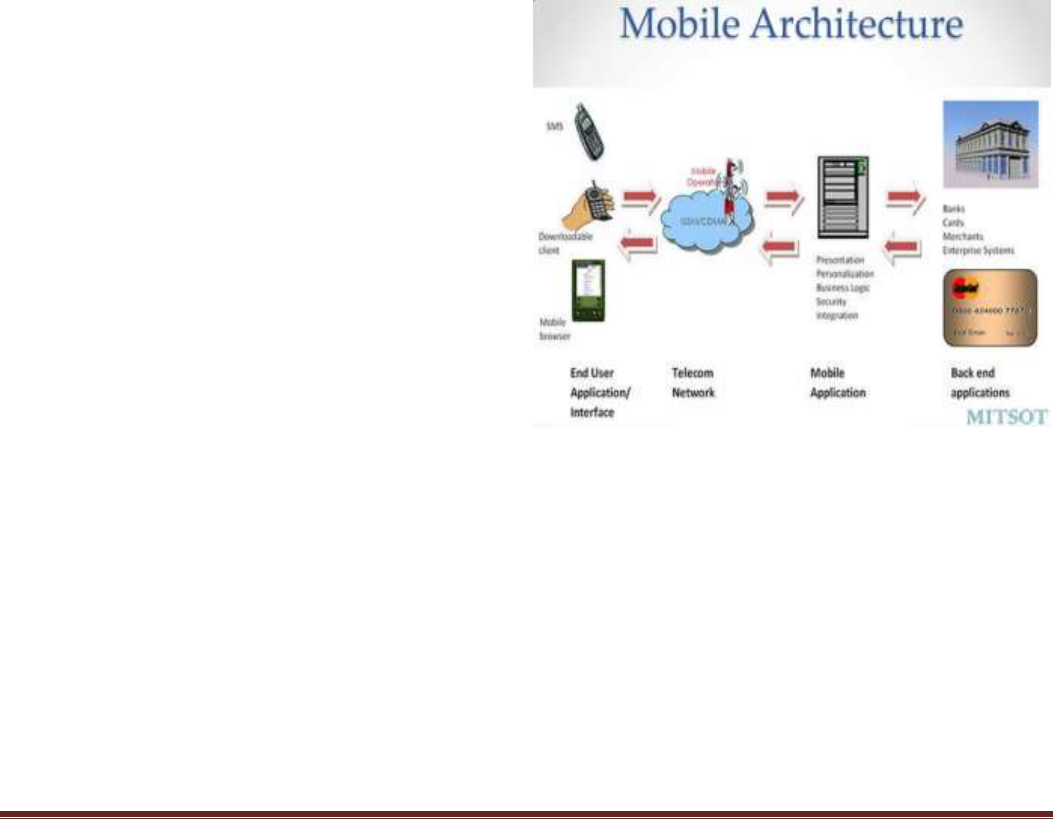
DOI: 10.18535/ijsrm/v5i7.26
Dr.G.Sasikumar, IJSRM Volume 5 Issue 07 July 2017 [www.ijsrm.in] Page 6015
Figure 1: Mobile Banking Architecture
be offered to customers are internet banking and mobile
banking systems, which allow customers to perform their
banking transactions [20]. Garrett has indicated that mobile
banking is the present and future need, paralley security is a
major issue [9]. Vaithilingam, Nair and Guru have investigated
that the adoption of mobile services in Malaysia and found
trust and security has a significant impact on the adoption of
mobile banking [15].
Amit Shankar and Pooja Kumari have been carried out to
know major factors which affecting mobile banking adoption
behaviour in different context. Secondly, quantitative
investigation is provided to support stated hypothesis.
Thereafter, results of reliability and validity test of constructs
are provided [22]. Sultan Y. As-Sultan, Ibrahim Ahmed Al-
have conducted study to
analyze the most well-known and accepted models to provide
a comprehensive understanding of their impacts toward the
adoption of mobile banking applications. In addition to that
the study exploring the most effective factors that have been
used to influence the goal of adoption behavior of mobile
banking applications and suggested some recommendations
for security of mobile banking[23].
3. Mobile Banking
3.1 Role of Mobile Phone
Mobile phones are playing vital role in daily walk of life of
large percentage of the world population. Communication
technology has left no aspect of human life untouched. Even
our morning alarm clocks have been replaced by the mobile
phones. Mobile phones have become a necessity for many
people throughout the world. The ability to keep in touch with
family, business associates, and access to email are only a few
of the reasons for the increasing importance of mobile phones.
Today's technically advanced cell phones are capable of not
only receiving and placing phone calls, but storing data, taking
pictures, and can even be used as walkie talkies, to name just a
few of the available options.
The enlarged uses of smart phones has increased demand for
m-banking services, prompting many more banks,
microfinance institutions, software houses, and service
providers to offer this innovative service together with new
sets of products and applications designed to extend their
client reach, improve customer retention, enhance operational
efficiency, increase market share, and provide new
employment opportunities[14]. Large types of mobile phones
and different operating systems are also a big challenge for
banks, as it is very difficult for them to provide standardized
applications. Convenience and security are two main factors
which can motivate other non-user to use technology based
banking services [5].
3.2 Importance of Mobile Banking
Mobile banking is the latest and most innovative service
offered by the banks. Mobile Banking is considered as a
mechanism which allows customer of a financial institution to
carry out various financial transactions with the help of their
mobile devices, such as Smart phones, notebooks or tablets.
With the increasing use of smart phone mobile banking is
catching up with the common customer [14]. Mobile
connectivity is vast and this makes mobile banking very
successful. The clients access their mobile banking facility
from a browser or a special application, enabling to view their
account balance, send remittances and perform most other
functions also available in standard e-banking facility. Many
experts say that mobile banking offers many benefits worth
using, and some are getting increasingly better. Information
technology has been exercised under two different paths in
banking. One is communication and connectivity and other is
business process [3], [7].
At present, banks have received wireless and mobile
technology into their assembly room to offer their customers
the freedom to pay bills, planning payments while stuck in
traffic jams, to receive updates on the various marketing
efforts while present at a party to provide more personal and
intimate relationships. Mobile devices are integrated with
multiple wireless communication technologies such as
Wireless Fidelity(Wi-Fi), Worldwide Interoperability for
Microwave Access (WiMAX), Bluetooth, Near Field
Communications (NFC), and a cellular interface which are
configured to use CDMA or GSM network schemes[7], [8].
Mobile banking functionality can be divided into three main
areas such as
(i) Informational Functions,
(ii) Transactional Functions and
(iii) Service, Marketing and Acquisition [17].
Owing to growth of Information and Communication
Technology the unethical hackers and anti-social elements are
interested to penetrate the online payments and money
transfer. The confidential information such as user name and
password must be maintained in secured manner to avoid
vulnerable and threats. Most of the banks try to make their
sites secured by implementing latest network security
software. The eminence of online banking services has
become a major region of attention among researchers and
bank managers owing to its strong impact on business
performance, profitability and customer service delivery.

DOI: 10.18535/ijsrm/v5i7.26
Dr.G.Sasikumar, IJSRM Volume 5 Issue 07 July 2017 [www.ijsrm.in] Page 6016
Figure 2: Mobile Banking Apps
Mobile Banking Service include:-
i). Mini statement.
ii). Monitoring of Term deposits.
iii). Ordering Cheque books.
iv). Balance checking in the account
v). Change of Pin.
vi). Blocking the lost ATM card.
vii). Fund Transfer.
viii). DTH Recharging.
ix). Purchasing ticket for a movie or travelling.
Mobile banking services are being offered through many
channels such as Short Messaging Services (SMS), Interactive
Voice Response (IVR), Mobile Application, and Wireless
Application Protocol (WAP), etc. Banks are taking advantages
of mobile innovation to provide its services to customers
economically and profitably. The introduction of m-banking
helps banks to perform its activity efficiently which lead to
consumer satisfaction and loyalty [3], [7].
3.3. Development of Mobile Banking Apps
Mobile banking apps has a short development history. Most
mobile banking service was offered over SMS banking up to
2010. Since 2010, with the success of iPhone and lightning
growth of Google Android, more banks started adapting a new
trend by launching mobile web based service and mobile
banking apps. According to a mini study by Mapa Research in
2012, upon a third of banks have their mobile detection on
their main site. Among the result, 61 percent of the mobile
optimized website has an option to download mobile banking
apps. Mobile banking apps is specifically designed for smart
phone and tablet, which run on OS.
Mobile banking apps is able to download from application
stores. Similar to online banking, mobile banking apps connect
connection, including Wi-Fi, 3G or data transfer, for complete
banking functionality[10]. When mobile phones turned into
smartphone, and began to mimic the power found in most
computers, banks have been able to provide consumers with
powerful mobile banking apps that allow customers to
complete their banking from wherever you are. This includes
making deposits, depending on the bank and its mobile app
checking funds, making bill payments, transferring or sending
money.
Latest all banks mobile apps launched in 2017.
i). Instant Money Transfer (IMT) Bank of India
ii). Kisan card AXIS BANK
iii). Bank of
Maharashtra
iv). M-Pesa ICICI + Vodafone
v). M-Wallet Canara Bank
vi). State Bank Freedom App State Bank of India
vii). Student Travel Card ICICI
viii). TAB BANKING FACILITY SBI
ix). Tap and pay ICICI
x). Twitter Handle account SBI
xi). Video conferencing Indusuld & federal bank
xii). Youth for India SBI
xiii).
SBI
xiv). IMobile app for windows phone ICICI
xv). ion
with American Express ICICI
xvi). RBL
Bank
xvii). Instant money transfer BOI
xviii). - Kotak
Mahindra Bank (KMB)
xix). - ICICI Bank
xx). anchayat - HDFC Bank
xxi). UPI App That Turns Your Smartphone into a Bank
for Easy Transfers RBI
xxii).
Mobile App State Bank Of India
xxiii).
App ICICI Bank
xxiv). Lakshmi Vilas Bank
Laxmi Vilas Bank
xxv). IMT APP (Instant Money transfer ) Launched By
State Bank Of India
xxvi). Ananya Project launched By Syndicate Bank
3.4. Pros and Cons of Mobile Banking
3.4.1.Pros of Mobile Banking
i). Mobile Banking uses the network of service provider
and it doesn't need internet connection. In a developing
countries like India where there is no internet connection
in the interiors there is the presence of mobile
connectivity.
ii). Mobile Banking is available round the clock 24/7/365
and is easy and convenient mode for many mobile users
in the rural areas.
iii). Mobile Banking is said to be more secured and risk
free than online/internet Banking.
iv). With the help of mobile banking you can pay your
bills, transfer funds, check account balance, review your
recent transaction, block your ATM card etc.
v). Mobile Banking is cost effective and Banks offer this
service at very low cost to the customers.
3.4.2. Cons of Mobile Banking
i). Though the security threat is less than internet banking,
mobile banking has security issues. One of the great
threats to mobile banking is "Smishing" which is similar

DOI: 10.18535/ijsrm/v5i7.26
Dr.G.Sasikumar, IJSRM Volume 5 Issue 07 July 2017 [www.ijsrm.in] Page 6017
to "phishing". In "Smishing" users receives fake
message asking for their Bank details. Many users have
fallen to this trap.
ii). Mobile Banking is not available on all mobile phone.
Some time it requires you to install apps on your phone
to use the Mobile Banking feature which is available on
high end smartphone. If you don't have a smartphone
than the use of Mobile Banking becomes limited.
Transaction like transfer of funds is only available on
high end phones.
iii). Regular use of Mobile Banking may lead to extra
charges levied by the bank for providing the services.
iv). Mobile phones are limited in processing speeds,screen
size and battery life. This act as a barrier in Mobile
Banking.
Like all other technology mobile banking has got it advantage
and disadvantage and up to users and how the users utilize
the technology. However there is no doubt that mobile
banking is take part significant role in every day banking
activities.
4 Cyber Crime
Cyber crime is defined as a combination of crime and
Many countries face difficulties in
addressing issues arising from cyber crimes, because they lack
a concrete definition of computer crimes and how such crimes
differ from traditional crimes[2],[12]. Cyber Crime is a
technique that employs ICT components like computer and
communication equipments etc. to harm the individual, trade,
government and ICT infrastructure. Schell and Martin define
suggested that the cyber-attacks against financial services
institutions are becoming more frequent and more
sophisticated [16], [18].
The weak and rigid authentication provided by signature,
PIN, pass-word and card security code in mobile banking has
numerous flaws and loop-holes [6]. Join Tom Wills, renowned
expert in global mobile trends, for insights into how global
banking institutions can navigate the mobile threat landscape,
including:
i). Emerging external threats to mobile banking and
payments;
ii). How to influence the riskiest wildcard user behaviour;
iii). Anti-fraud solutions and strategies to prevent mobile
attacks and maintain customer trust.
Cyber attacks are classified in to several types [13]. They are
i). User based / against a Persons
ii). Property based cyber crimes
iii). Society based cyber crime
iv). Private Organizations based
v). Government based cyber crime.
5 Mobile Banking Security
Security is the foundation for the development of mobile
banking. Only when the security is fully shielded, the mobile
banking can deal with other traditional banking business
activities. The security and privacy of personal information
remain common concerns for mobile phone users, and many
smartphone users reported taking steps to guard against
possible risks. Even the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) that is
the main body, has been issuing various directions and
recommendations from time to time to strengthen cyber
security of banking operations in India.
5.1. Preventive Measures for Cyber Crime
In order to protect banking transactions from frauds and other
threats, some preventive measures are suggested. They are
i). Make sure with a protection program that gives power
over cookies that forward information back to Web sites.
ii). Bring into play latest anti-virus software, operating
systems, Web browsers and email programs
iii). Place firewall and develop your content off line.
iv). Forward credit card information just to safe and sound
web sites
v). If Web site serves up active content from a database,
consider putting that database behind a second interface
on your firewall, with tighter access rules than the
interface to your server.
vi). Ac
vii). Only use the most up-to-date system version of your
mobile device
viii). If possible, use up-to-date virus protection software and a
personal firewall
ix). Turn on Blue Tooth or enable Internet only when
required.
x). Do turn off the wireless connections when not needed.
xi). Regularly update the cell phone software.
xii). Install latest Anti Virus Software, and keep it updated.
xiii). Use strong passwords to lock your cell phone.
xiv). Never share personal information with stranger
xv). Never store personal banking details in cell phones.
xvi). Be suspicious while entertaining strangers on social
networking website.
xvii). While banking and shopping online, ensure the sites are
https or shttp.
6 Conclusion
Security around the transfer of data through communication
channels is a challenge for developers, they noted, pointing out
that developers are placing too much confidence in secure
end-user behavior and back-end server-side communications.
Even now many customers are uncomfortable with online
banking regarding with security. In addition to that cyber
criminals are trying day by day to find new techniques to avail
unauthorized access to finances of financial institutions,
banking customers.
In developing countries, electronic crime is a serious problem
because there is a lack of training on the subjects to investigate
the electronic crime. Precaution is the only way to maintain
secured transactions in this mobile banking system. There is a
need to bring changes in the Information Technology Act to
make it more effective to fight cyber crime. Mobile banking
services play a significant role in improving customer
satisfaction in high level and it has its own impact on customer
satisfaction.

DOI: 10.18535/ijsrm/v5i7.26
Dr.G.Sasikumar, IJSRM Volume 5 Issue 07 July 2017 [www.ijsrm.in] Page 6018
References
[1] Schell, B. & Mart
rbara: ABC-CLIO, 2004.
[2] Aslan.Y. Global Nature of Computer Crimes and the
Convention on Cyber Security. Ankara Law Review,
Vol. 3 No. 2, 129-142, 2006.
[3] Laukkanen.T.,
Process Management Journal; vol. 13 No. 6, pp. 788-
797, 2007.
[4] Bangens. L., & Soderberg.B, Mobile banking-Financial
services for the unbanked, 2008.
[5] Comninos A, Esselaar S, Ndiwalana A, Stork C
Towards evidence-based ICT policy and regulation m-
banking the un
[6] Edge, M A survey of
signature based methods for financial fraud detection.
Computers & security, 28(6), 381-394, 2009.
[7] Quick.C.
opportunity for ma
[8] Alex.K., Is it finally time for M-Commerce,2010.
[9] Garrett, J., Mobile banking security, Credit Union
Magazine, 24-28. Retrieved from
http://www.creditunionmagazine.com/articles/37367-
mobile-banking-security, 2011.
[10] Mapa Research., How the world's top banks handle
mobile device detection.URL:
http://www.maparesearch.com., 2012
[11] Duggal.P., Mobile Banking and Mobile Law, 2013.
[12] Mayunga.J. Cybercrimes Investigation in Tanzania.
Morogoro: Mzumbe University, 2013.
[13] Raksha Chouhan, Shashikant Pardeshi,
Journal of Engineering, Science And Management
Education (JESME), Quarterly Research Journal of
NITTTR Bhopal, Vol-6, Issue- III, JulySeptember
2013, PP 131-136.
[14] Shaikh.A.A., Mobile banking adoption issues in
Pakistan and challenges ahead. J. Inst. Bankers Pak. 80
(3), 1215, 2013.
[15] Vaithilingam, S., Nair, M., & Guru, B. K. . Do trust and
security matter for the development of M-banking?
Evidence from a developing country. Journal of Asia-
Pacific Business, 14(1), 4-24,2013
[16] Cuomo A. M., Report on Cyber Security in the
Banking Sector. New York State Department of
Financial Services, 2014.
[17] Pegueros.V.,Security of Mobile Payment and Banking.
URL:http://www.sans.org/reading-room/whitepapers
/ecommerce/security-mobile-banking-payments-34062.
Accessed: 12 Dec 2014.
[18] Ryan W. J., A Resource Guide for Bank Executives:
Exec-utive Leadership of Cyber rence
of State Bank Supervisors, 2014.
[19] J. Tellez Isaac and Z. Sherali, "Secure Mobile Payment
Systems," IT Professional, vol. 16, pp. 36-43, 2014.
[20] T.Wai-Ming and L. S. L. Lai, "Mobile Banking and
Payment in China," IT Professional, vol. 16, pp. 22-27,
2014.
[21] A. A. Shaikh and H. Karjaluoto, "Mobile banking
adoption: A literature review," Telematics and
Informatics, vol. 32, pp. 129-142, 2015.
[22] Amit Shankar and Pooja Kumari Factors Affecting
Mobile Banking Adoption Behavior in India Journal
of Internet Banking and Commerce, vol. 21, no. 1.,
2016
[23] Sultan Y. As-Sultan, Ibrahim Ahmed Al-
Journal of Advanced Research in Computer Science
and Software Engineering, Volume 7, Issue 2, February
2017.
Author Profile
Dr.G.SASIKUMAR is working as Assistant Professor in
Economics and Research Advisor in the PG Dept. of
Economics and Management Studies, Maruthupandiar
College of Arts & Science, Vallam, Thanjavur, Tamilnadu,
India. He has completed his M.A. Economics in A.V.V.M.Sri
Pushpam College affiliated to Bharathidasan
University,Trichy, TamilNadu, India in the year 2000 and
M.Phill in Economics in Annamalai University in the year
2002. He has received his Ph.D in
Economics from Bharathidasan
University, Trichy in the year
2010. Also he has finished his
MBA in Finance in Rajah Serfoji
Govt. College affiliated to
Bharathidasan University in the
year 2017.
Honorable Puthucherry Chief
Minister NARAYANASAMY at Puthucherry on 26.03.2017
organized by Top International Educational Trust-TIESFA-
2017. He has 15 years of teaching experience at PG level in
the field of Economics and Management Studies. He has
published two research papers in International Journals and
presented many papers in the National and International
conferences. Also he has published three books with ISBN
Number. His areas of research interest include Finance,
Environmental Economics, Agricultural Economics, and
Microeconomics.
